In the ever-evolving landscape of technology investments, semiconductor exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have garnered significant attention due to their exposure to the rapidly growing semiconductor industry. Two prominent ETFs, the VanEck Vectors Semiconductor ETF (SMH) and the iShares PHLX Semiconductor ETF (SOXX), have demonstrated contrasting performances despite their similar focus on semiconductor companies. Understanding the factors behind the differing performance of these two ETFs provides valuable insights for investors looking to capitalize on the semiconductor industry’s growth potential.
**Diverse Holdings:**
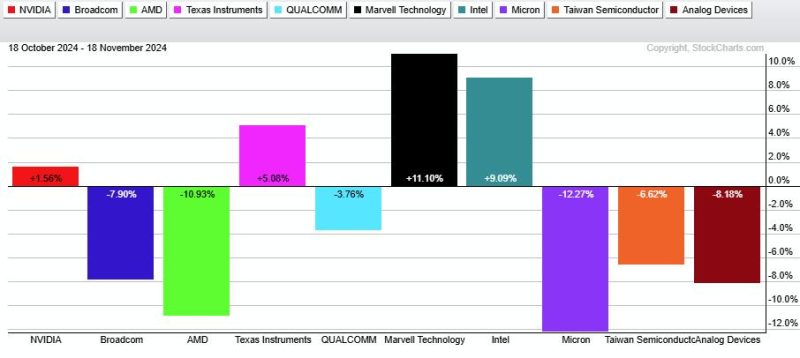
One key factor contributing to the varying performance of SMH and SOXX lies in their underlying holdings. SMH, with over 25% of its assets allocated to its top two holdings, Intel and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), displays a more concentrated portfolio compared to SOXX. On the other hand, SOXX maintains a more diversified approach, with its top ten holdings accounting for about half of its assets. This difference in portfolio composition has implications for each ETF’s performance during market fluctuations, with SMH’s concentrated exposure potentially leading to amplified movements in response to specific company performance or industry trends.
**Global Supply Chain Dynamics:**
The semiconductor industry operates within a complex global supply chain where geopolitical events and macroeconomic factors can significantly impact companies’ revenues and profitability. Recent disruptions in the supply chain, such as semiconductor shortages and trade tensions, have underscored the importance of considering global dynamics when investing in semiconductor ETFs. SMH’s holdings in companies with diverse geographic footprints, such as TSMC with its presence in Taiwan and the United States, may provide a level of resilience compared to SOXX’s more US-centric portfolio. By diversifying across regions, SMH could potentially better weather supply chain disruptions or regulatory changes affecting specific countries or regions.
**Technology Trends and Innovation:**
Another crucial aspect influencing the performance of semiconductor ETFs is their exposure to emerging technology trends and innovation within the industry. As semiconductor companies race to develop cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, 5G, and autonomous vehicles, the ability to stay ahead of these trends becomes paramount for sustained growth. Both SMH and SOXX feature holdings in leading-edge companies at the forefront of technological innovation. However, differences in the weighting of these companies within each ETF can result in varying responses to shifts in technology trends. Investors seeking exposure to specific technological advancements may benefit from analyzing the portfolio composition of SMH and SOXX to identify the ETF that aligns closely with their investment thesis.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, the tale of two semiconductor ETFs, SMH and SOXX, highlights the importance of considering factors such as portfolio concentration, global supply chain dynamics, and exposure to technology trends when evaluating investments in the semiconductor industry. While both ETFs offer investors access to a diverse range of semiconductor companies, their distinct characteristics can lead to differing performances in response to market conditions and industry developments. By conducting thorough research and understanding the nuances of each ETF, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment objectives and risk tolerance in the dynamic world of semiconductor investments.